-
Products
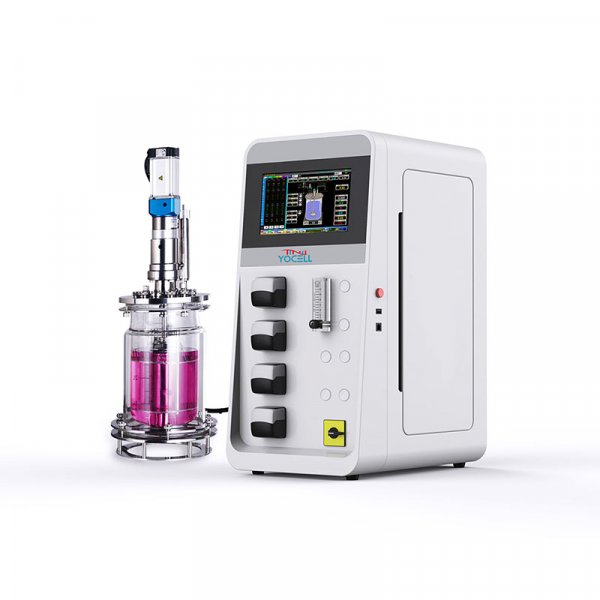
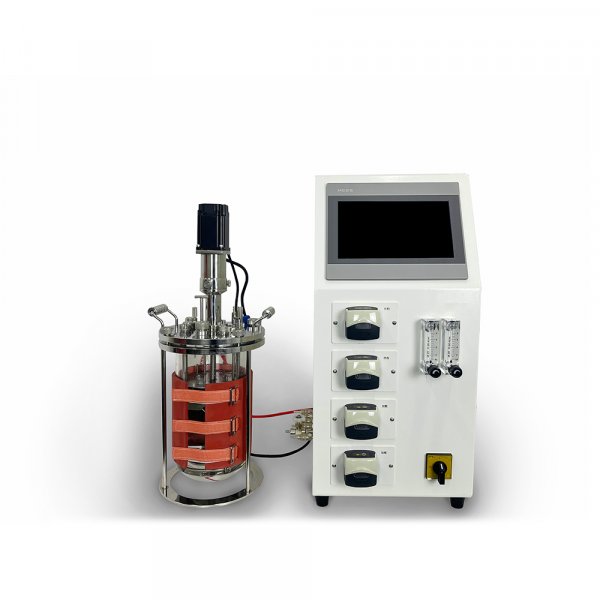
- Bioreactor / Fermentor
- Centrifuge
- Homogenizer
- Filtration System
- Chromatographic System
-
Filling & Packaging
- Cleaning & Sterillization
-
Filling & Closing
- Filling and stoppering machine
- Filling, stoppering and capping machine
- Ferrule capping machine
- Oral liquid filling and capping machine
- Star wheel positioning type capping machine
- Filling and capping machine
- Spray filling and capping machine
- Powder filling and capping machine
- Filling and screw capping machine
- Single knife high-speed capping machine
- Cupping machine
- Loading
- Lableing
-
All Complete Lines
- Sterile eye drop production line
- Oral liquid production line
- Diagnostic reagent filling production line
- Vaccine production line
- Infusion bottle filling line
- Gargle filling line
- Plastic bottle syrup production line-3
- Plastic bottle syrup production line-2
- Plastic bottle syrup production line-1
- Glass bottle syrup production line
- General laboratory equipment
- Sterile tube sealing/welding equipment
- Freeze-drying equipment
- Spray Dryer
- Reactor
- Solutions
- Service Support
- News & Events
- About Us
- Contact